May 24, 2022
It’s time to shine a light on a little talked about but common result of systemic lupus-lupus nephritis.
- Lupus affects 1.5 million adults in the U.S.
- In adults with lupus, 50% will have kidney disease
- Between 1 and 3 out of every 10 people with lupus nephritis will develop kidney failure
Download the lupus nephritis fact sheet.
What is lupus?
Lupus is an autoimmune disorder, meaning it is caused when the immune system turns against the body. There is no clear cause of lupus; however, family history, infections or viruses, and environmental factors like toxic chemicals or pollution, may play a role.
There are two main types of lupus:
- Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): This form can cause harm to the skin, joints, kidneys, and brain.
- Discoid lupus erythematosus: Discoid lupus only affects the skin.
How does lupus cause kidney damage?
People with lupus experience swelling, and in some cases, this inflammation extends to the kidneys. If this happens, the small filters in the kidneys, called glomeruli, become damaged and can’t filter out wastes properly.
Learn more about lupus and your kidneys.
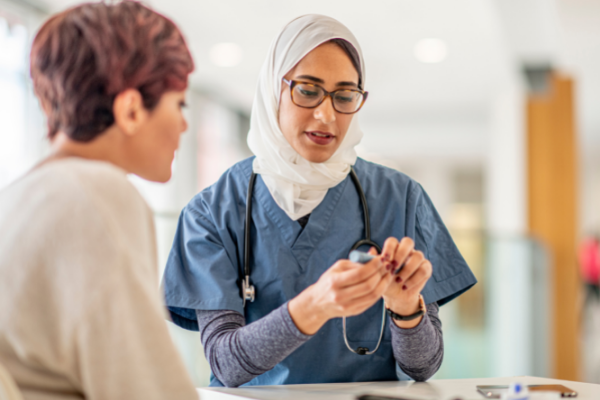
How do I know if I have lupus or lupus nephritis?
There are no standard tests to diagnose lupus symptoms vary from person to person. If lupus is suspected, a rheumatology specialist will often get involved to confirm the diagnosis.
To determine whether or not you have lupus nephritis, your doctor will review your medical background, family history, and symptoms, including:
- Blood in the urine (hematuria): Your kidneys are supposed to stop blood cells from getting into your urine – if this occurs, your urine may look pink or light brown from blood
- Proteinuria or higher than normal levels of protein in the urine
- Swelling due to fluid buildup in the ankles, legs, or eyes
- Unexplained weight gain
- High blood pressure
- Inflammation or scarring of the kidneys
- Fatigue
Doctors may request urine samples to test for protein and blood, blood tests to determine eGFR, and a kidney biopsy.
Treating lupus and lupus nephritis
Since the body’s immune system is attacking the body, drugs like steroids and antimalarials are used to block the body’s immune system. However, everyone is unique, which means a combination of therapies may be needed to manage symptoms, including:
- Corticosteroids and immunosuppressive drugs: These drugs help calm the immune system down.
- Monoclonal antibodies: Artificial proteins that work as antibodies against one specific substance.
- ACE inhibitors and ARBs: Blood pressure medication helps reduce protein loss through urine.
- Diuretics: Helps remove excess fluid.
- Diet change: Some diet changes may be needed to take some burden off the kidneys. For example, following a diet low in sodium, fat, and protein helps manage blood pressure to help prevent long-term kidney damage.
Your doctor will help you find a treatment plan that is right for you.